Body
How can body therapy nourish you?
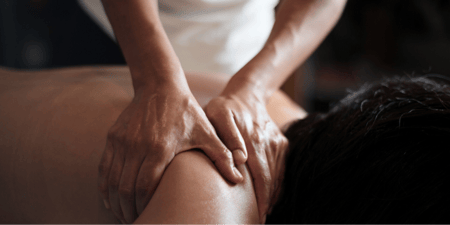
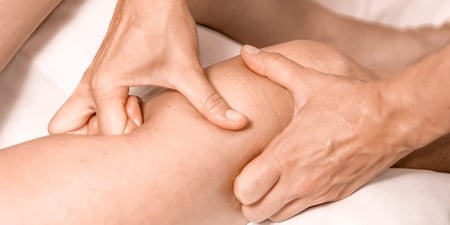
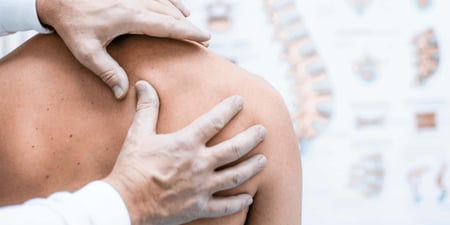
Body therapy, often also called bodywork, involves hands-on manipulative techniques that improve the function of the musculoskeletal system, and may consequently affect other bodily systems. The various bodywork modalities are associated with different parts of the body, or different approaches to treatment.
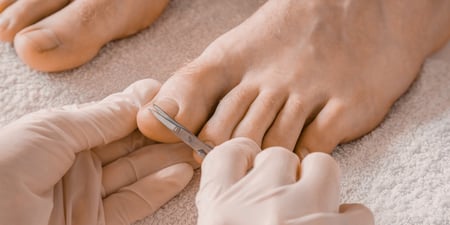
For example, chiropractors can be described as “musculoskeletal practitioners with a special emphasis on spinal pain[1]”, while podiatry is concerned with the health of the feet and legs. Osteopathy involves moving and stretching the limbs as well as the torso to help support the body’s innate healing ability[2]. Physiotherapy, on the other hand, is focused on relieving pain and restoring as much natural function as possible[3] to parts of the body affected by disability, illness or injury.
Benefits of body therapy
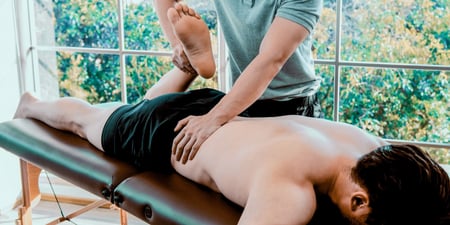
Research suggests physiotherapy may be a reliable alternative to surgery or medication[4] for managing pain and improving mobility after illness or injury. Physiotherapy is often used to help people with disability with evidence to suggest it may improve the mobility and coordination[5] of people suffering from Parkinson’s disease. It is also reported that physiotherapy may make it easier for people with multiple sclerosis to coordinate voluntary movement[6].
Research indicates chiropractic may help relieve migraine[7], as well as possibly being one of several modalities that can reduce chronic lower-back pain[8]. Osteopathy is reported to possibly reduce bowel discomfort[9] in people with a history of Crohn’s disease, and it may also reduce the length of time premature babies require hospital care[10].
What to expect from a body therapy session
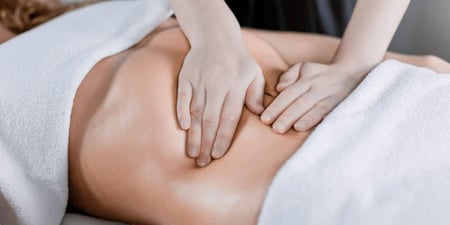
The common theme in most types of body therapy is that the practitioner works with you to help you align your musculoskeletal system and restore its optimal function[11]. Although the details will depend on the particular modality, your first session will start with your practitioner asking about your medical history and the health concern that has prompted you to seek treatment.
They will perform an assessment or diagnosis, for example by observing the way you walk[12] or testing your range of movement[13] in an affected joint. Your practitioner will treat you using massage, stretches, spinal adjustment or other techniques, or help you do exercises to restore or improve mobility. At the end of each session, you will often be prescribed further exercises to do at home, and you may be given a written document outlining your care or treatment plan.
As with any exercise or wellness program, please consult your medical professional before commencing body therapy. If you have an injury or other health issue, or any concerns at all, also speak to your practitioner, who will be happy to address these and advise you whether the modality in which they specialise is a good treatment option for your individual requirements.
References
1. Walker BF. The new chiropractic. Chiropractic & Manual Therapies; 2016.
2. Osteopathy. Better Health Channel; [cited on 2024 Dec 6].
3. Physiotherapy. Allied Health Professions Australia; [cited on 2024 Dec 6].
4. How does physical therapy help? Medical News Today; 2024.
5. Banks MA, Caird F. hysiotherapy benefits patients with Parkinson’s disease. Clinical Rehabilitation; 1989.
6. Armutlu K, Karabudak R, Nurlu G. Physiotherapy approaches in the treatment of ataxic Multiple sclerosis: a pilot study. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair; 2001.
7. Bryans R, Descarreaux M, Duranleau M, Marcoux H, Potter B, Ruegg R, et al. Evidence-Based Guidelines for the Chiropractic Treatment of Adults with Headache. Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics; 2011.
8. Spinal manipulative therapy for chronic low-back pain. Cochrane; 2021.
9. Piche T, Pishvaie D, Tirouvaziam D, Filippi J, Dainese R, Tonohouhan M, et al. Osteopathy decreases the severity of IBS-like symptoms associated with Crohn’s disease in patients in remission. European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology; 2014.
10. Piche T, Pishvaie D, Tirouvaziam D, Filippi J, Dainese R, Tonohouhan M, et al. Osteopathy decreases the severity of IBS-like symptoms associated with Crohn’s disease in patients in remission. European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology; 2014.
11. What to expect from an Osteopath Treatment. Body & Health Creation; 2018.
12. Biomechanical and gait assessment. The Walking Clinic; [cited on 2024 Dec 6].
13. Physiotherapy FAQs. Nuffield Health; [cited on 2024 Dec 6].